PMOS Transistor
Symbol
Information
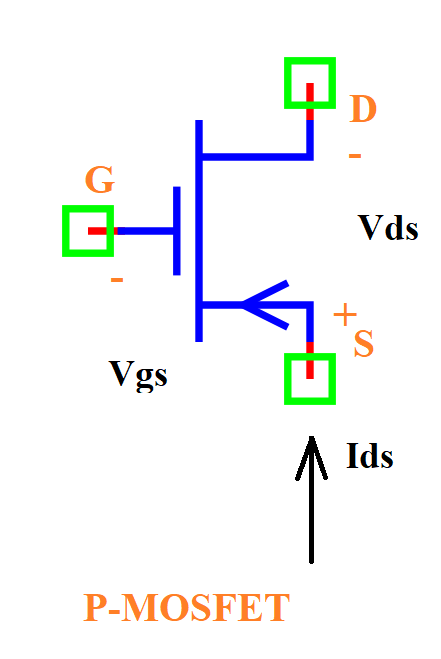
A P-channel MOSFET (PMOS) is a type of MOSFET where the majority charge carriers are holes. It operates with a negative gate-to-source voltage (Vgs) and conducts when Vgs is lower than the threshold voltage (Vt).
The behavior of a PMOS transistor is divided into three regions:
Cutoff Region: When |Vgs| < |Vt|, the transistor is off, and no current flows.
Triode Region: When |Vgs| > |Vt| and |Vds| is small, the transistor behaves like a resistor.
Saturation Region: When |Vgs| > |Vt| and |Vds| is large, the transistor is fully on, and the current is limited by channel resistance.
Ports
d: Drain terminal
g: Gate terminal
s: Source terminal
Model
The PMOS model implements an ideal P-channel MOSFET.
A PMOS transistor allows current to flow from the source to the drain when the gate-source voltage is sufficiently negative.
Attributes:
Vgs (signal): Gate-Source voltage, defined between nodes (s, g).
Vds (signal): Drain-Source voltage, defined between nodes (s, d).
Id (signal): Drain current, defined between nodes (s, d).
Ig (signal): Gate current, assumed to be zero for an ideal MOSFET.
Kp (param): Transconductance coefficient, default 200 μA/V².
W (param): Channel width, default 100 μm.
L (param): Channel length, default 100 μm.
Vt (param): Threshold voltage, default 0.5 V.
lambd (param): Channel-length modulation parameter, default 0.0.
Methods:
analog(): Defines the PMOS transistor behavior in different operating regions.
from pyams.lib import model, signal, param, voltage, current
class PMOS(model):
"""
Ideal P-channel MOSFET model.
"""
def __init__(self, d, g, s):
# Signal declaration
self.Vgs = signal('in', voltage, s, g)
self.Vds = signal('in', voltage, s, d)
self.Id = signal('out', current, s, d)
self.Ig = signal('out', current, g, '0')
# Parameter declaration
self.Kp = param(200e-6, 'A/V^2', 'Transconductance coefficient')
self.W = param(100.0e-6, 'm', 'Channel width')
self.L = param(100.0e-6, 'm', 'Channel length')
self.Vt = param(0.5, 'V', 'Threshold voltage')
self.lambd = param(0.000, '1/V', 'Channel-length modulation')
def analog(self):
"""Defines the MOSFET's behavior in different operating regions."""
K = self.Kp * self.W / self.L
self.Ig += 0.0
# Cutoff Region: Vgs <= Vt
if self.Vgs <= self.Vt:
self.Id += 0.0
# Saturation Region: Vgs - Vt < Vds
elif (self.Vgs - self.Vt) < self.Vds:
self.Id += K * (self.Vgs - self.Vt) ** 2 * (1 + (self.lambd * self.Vds)) / 2
# Triode Region: Vgs - Vt >= Vds
else:
self.Id += K * ((self.Vgs - self.Vt) - (self.Vds / 2)) * (1 + (self.lambd * self.Vds)) * self.Vds
Command syntax
The syntax for defining a PMOS transistor in a PyAMS simulation:
# Import the model
from pyams.models import PMOS
# Tname: is the name of the PMOS instance
# d, g, s: The connection points in the circuit
Tname = PMOS(d, g, s)