BJT Characteristics Analysis
Introduction
A Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is a semiconductor device used for amplification and switching applications. In this document, we analyze the collector current (I:sub:`C`) versus collector-emitter voltage (V:sub:`CE`) characteristics for different base currents (IB).
Equations
The fundamental equation governing the BJT in active mode is:
where:
\(I_C\) is the collector current,
\(I_B\) is the base current,
\(\beta\) is the current gain of the transistor.
The collector-emitter voltage is given by:
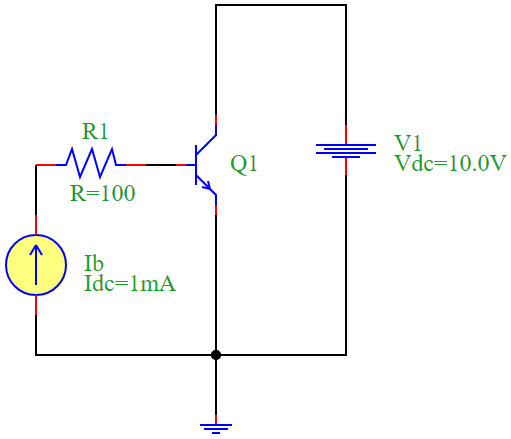
Circuit Description
The circuit consists of:
A DC current source supplying base current (\(I_B\)),
A DC voltage source (\(V_{CC}\)),
An NPN transistor (\(Q_1\)),
A resistor (\(R_1\)) to limit base current.
Circuit Diagram
Simulation Results
The results obtained from the simulation show how the collector current varies with the collector-emitter voltage for different base currents.
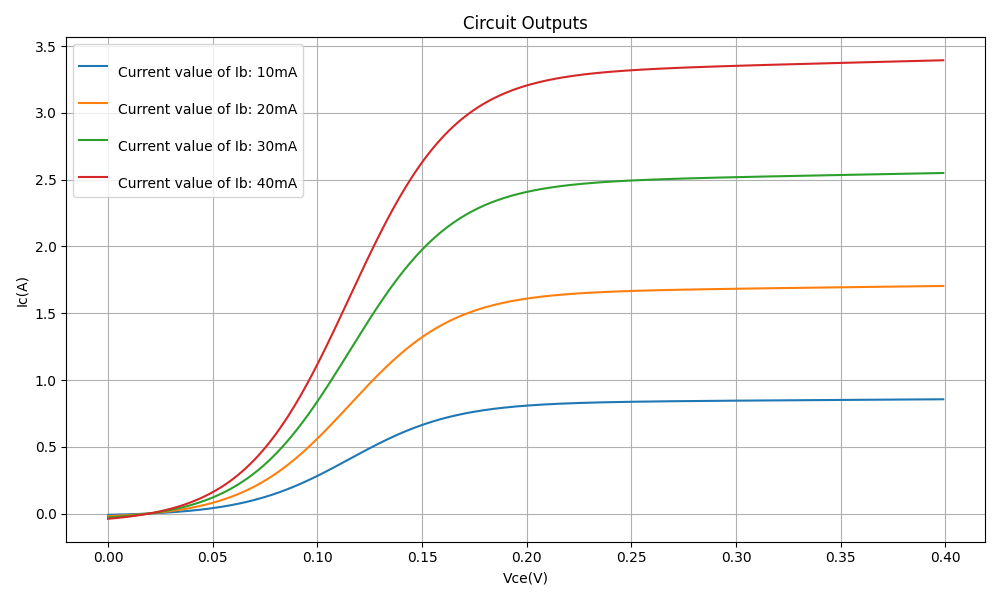
Conclusion
This simulation provides insights into the BJT’s behavior under different base currents, demonstrating its amplification properties. The collector current increases with base current, confirming the fundamental transistor operation principle.